Ovarian Cysts Treatment
Ovarian cysts are common growths that develop on or inside your ovaries. There are several types of cysts. The most common kinds are harmless, don’t cause symptoms and eventually go away without treatment. Rarely, cysts can cause complications that require your provider’s attention. Getting regular pelvic exams can help reduce your chances of experiencing problems with a cyst.
What is an ovarian cyst?
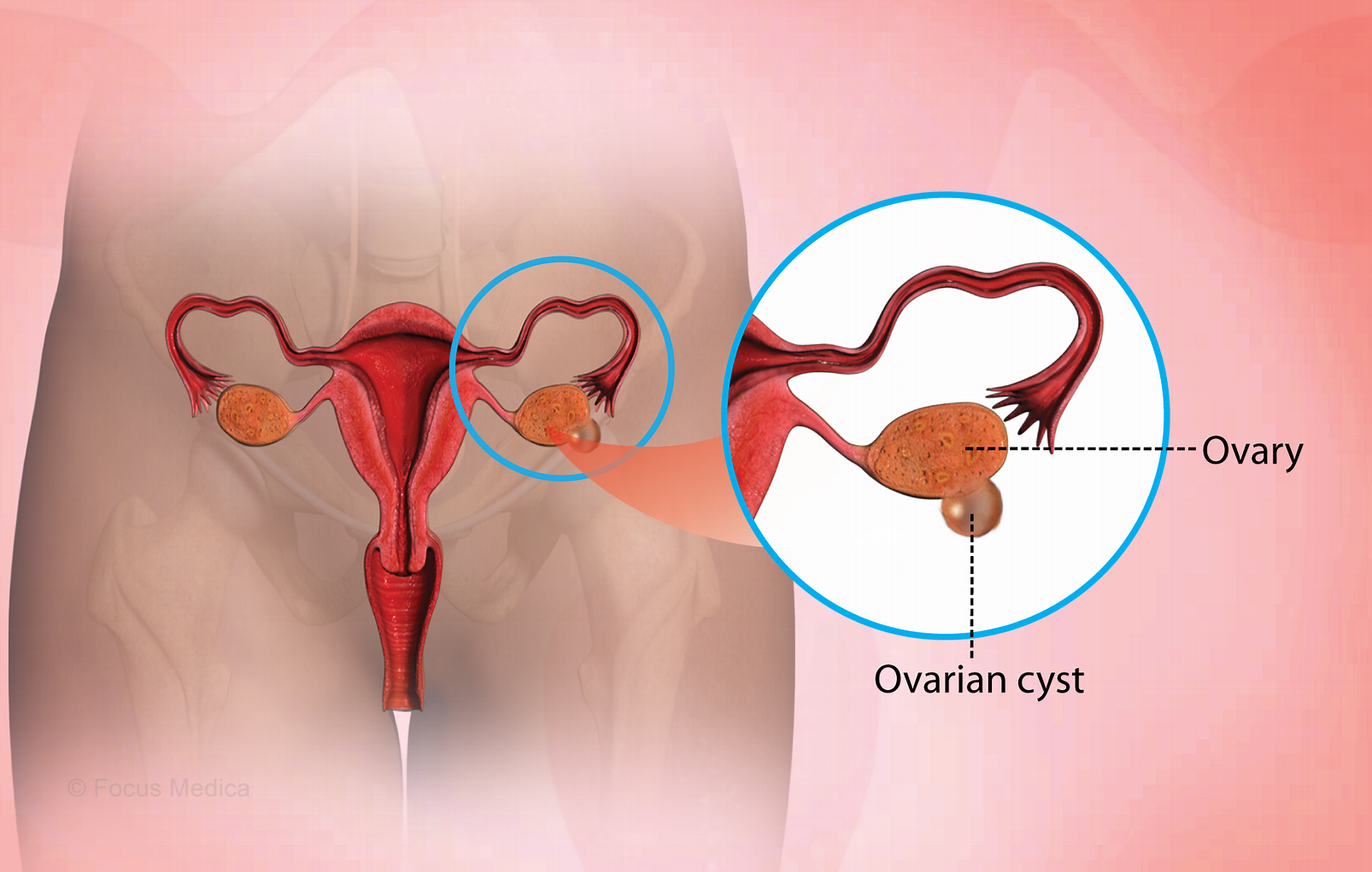
An ovarian cyst is a sac filled with fluid or semisolid material that forms on or within one or both of your ovaries. Your ovaries are small organs in your pelvis that hold egg cells and make hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone.
There are different types of ovarian cysts, most of which are painless and harmless (benign). Usually, ovarian cysts don’t cause symptoms. You likely won’t know you have one unless your provider finds one during a routine pelvic exam or imaging procedure.
Rarely, ovarian cysts can cause complications. Scheduling regular pelvic exams and speaking with your provider about any symptoms you may be experiencing can help prevent any problems with a cyst.
What are the types of ovarian cysts?
Most ovarian cysts are functional cysts. They form in response to your body’s changes during your menstrual cycle. Less commonly, ovarian cysts form for reasons unrelated to menstruation.
Functional cysts
Functional cysts are the most common type of ovarian cyst and aren’t disease-related. They occur as a result of ovulation (the release of an egg from the ovary). These cysts can be a sign that your ovaries are functioning as they should. Functional cysts generally shrink over time, usually within 60 days, without specific treatment.
- Follicular cysts. A small sac in your ovary, called a follicle, releases an egg each month as part of your menstrual cycle. A follicular cyst forms when the follicle doesn’t release an egg. Instead, the follicle fills with fluid and grows bigger.
- Corpus luteum cysts. After the follicle releases an egg, it forms a hormone-producing group of cells called the corpus luteum. A cyst forms when fluid collects in the corpus luteum, causing it to grow.
Sometimes, functional cysts are called simple cysts.
Other cysts
Not all ovarian cysts form in response to your menstrual cycle. They aren’t always signs of disease, but your provider may want to monitor them to ensure that they don’t cause complications. They include:
- Cystadenomas. These cysts form on the surface of your ovary. They can be filled with fluid that’s thin and watery or thicker and mucous-like.
- Dermoid cysts (teratomas). Dermoid cysts consist of cells that make up all types of tissue in the human body, ranging from skin, hair, teeth and even brain tissue.
- Endometriomas. These cysts are filled with endometrial tissue, the same tissue that you bleed each month during your period.
- Ovarian cancer. Unlike the conditions above, ovarian cancer cysts (tumours) are solid masses of cancer cells.
Who is affected by ovarian cysts?
Anyone with ovaries can develop an ovarian cyst. Your chances increase based on your:
- Age. Ovarian cysts are more common if you haven’t gone through menopause.
- Pregnancy status. Cysts are more likely to form and remain during pregnancy.
- History of ovarian cysts. You’re more likely to have an ovarian cyst if you’ve had one before.
- Current medical conditions. You’re more likely to get an ovarian cyst if you have: endometriosis, hormone problems or if you’re taking medications to help with ovulation, like clomiphene (Clomid©).
How common are ovarian cysts?
Ovarian cysts are extremely common, especially if you haven’t gone through menopause yet. Functional cysts are the most common type of ovarian cyst.
Are ovarian cysts serious?
Usually, no. Most ovarian cysts are harmless, and they often go away on their own eventually. Some types of cysts are more likely to become cancerous or cause complications, but this is rare. Less than 1% of ovarian cysts are cancerous. And your provider can monitor any concerning cysts closely to reduce your risk of experiencing complications.
What causes an ovarian cyst?
Ovulation is the leading cause of ovarian cysts. Other causes include:
- Abnormal cell reproduction. Atypical cell reproduction can cause cysts like dermoids and cystadenomas to form.
- Endometriosis. These cysts often form on the ovary in the advanced stages of endometriosis.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). Severe pelvic infections can spread to your ovaries, causing cysts.
What are the signs and symptoms of an ovarian cyst?
Some smaller cysts cause no symptoms. In these cases, you may not even know you have a cyst. Larger cysts may cause:
- Pelvic pain or a dull ache in your back.
- A feeling of fullness (bloating) located in your lower belly may feel more pronounced on one side of your body.
- Pain during intercourse (dyspareunia).
- Painful periods.
Symptoms that linger could indicate a condition called polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). PCOS is a condition that causes irregular periods and other hormone-related problems, including obesity and infertility. Other symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome include hirsutism (increased growth of body hair) and difficulty losing weight.
What does it feel like when you have a cyst on your ovary?
The experience of having an ovarian cyst varies from person to person. You may feel:
- No pain at all.
- Mild discomfort or a feeling of fullness.
- Pain that could be described as sharp or like a dull ache.
- Discomfort or pain that comes and goes without explanation.
Can you gain weight with an ovarian cyst?
Yes. Cysts can cause bloating, which contributes to weight gain. Some cysts secrete hormones that can cause you to gain weight.
What are the complications of an ovarian cyst?
- Cancerous cyst. Ovarian cysts that develop after menopause are more likely to be cancerous than cysts that form before menopause.
- Ruptured ovarian cyst. Functional cysts commonly rupture without causing any negative symptoms. But sometimes, a ruptured cyst can cause severe pain and swelling in your belly. The larger it is, the greater likelihood it has of breaking.
- Ovarian torsion. Cysts can grow so big that they distort the shape of your ovary, increasing the likelihood that it’ll twist. The twisting can prevent blood flow to your ovary, causing it to die. Extreme pain, nausea and vomiting are all signs of ovarian torsion.
Seek medical assistance right away if you’re experiencing the symptoms of a ruptured ovarian cyst or ovarian torsion.
How is an ovarian cyst diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will first rule out pregnancy as the cause of your symptoms. Then, they may use the following tests to diagnose an ovarian cyst:
- A pelvic exam: Your provider will feel inside your pelvis for any lumps or changes.
- Ultrasound: This imaging procedure uses sound waves to create images of your body's internal organs. It can detect cysts on your ovaries, including their location and whether they’re primarily fluid or solid.
- Laparoscopy: This is a procedure performed in an operating room. Your provider inserts a camera through an incision (cut) in your abdomen and can view your reproductive organs and pelvic cavity. If your provider diagnoses a cyst at this time, they can remove it.
How is an ovarian cyst treated?
Treatment will depend on factors like your age, your symptoms and what’s likely causing your cyst.
Watchful waiting: Functional ovarian cysts usually go away without treatment. If your cyst is likely functional, your provider may suggest a wait-and-see approach. You may have a follow-up ultrasound within a few weeks or months after your diagnosis to see if your cyst has resolved on its own.
Ovarian cyst medications: Your provider may give you medications containing hormones (such as birth control pills) to stop ovulation and prevent future cysts from forming.
Ovarian cyst surgery: If a cyst is causing symptoms and getting bigger, you may need surgery to remove it. The type of surgery depends on the size of the cyst and how it appears on the ultrasound. The different procedures used include:
- Laparoscopy: This is a procedure where your provider inserts a small camera through a small incision in your abdomen. They view your reproductive organs and pelvic cavity using the device. The ovarian cyst can be removed through tiny incisions (ovarian cystectomy).
- Laparotomy: Your provider may perform this procedure if the cyst is very large or if there are other concerns.
If your provider suspects cancer, they may consult with a cancer specialist, or gynecological oncologist, about the best treatment options for you.
When should I call my healthcare provider?
Call your healthcare provider if any of the following occur:
- Your menstrual periods are late, irregular, or painful.
- Your abdominal pain doesn't go away.
- Your abdomen becomes enlarged or swollen.
- You have trouble urinating or emptying your bladder.
- You have pain during intercourse.
- You have feelings of fullness (bloating), pressure, or discomfort in your abdomen.
- You lose weight for no apparent reason.
- You feel generally ill.
Get help immediately if you notice signs of ovarian torsion:
- Severe abdominal pain that comes on suddenly, accompanied by vomiting or fever.
- Feeling light-headed or faint and breathing rapidly.
- Cold, clammy skin.
The Chawla IVF medical team at Chawla Nursing Home understands the risks and rewards that come with ovarian cysts, and we will help you through every step of the way. Schedule a consultation appointment with one of our doctors at our Jalandhar location to find out if ovarian cysts are your best option for prevention purposes.
Schedule An Appointment
Get your Appointment Confirm with us Easily

