Ectopic Pregnancy
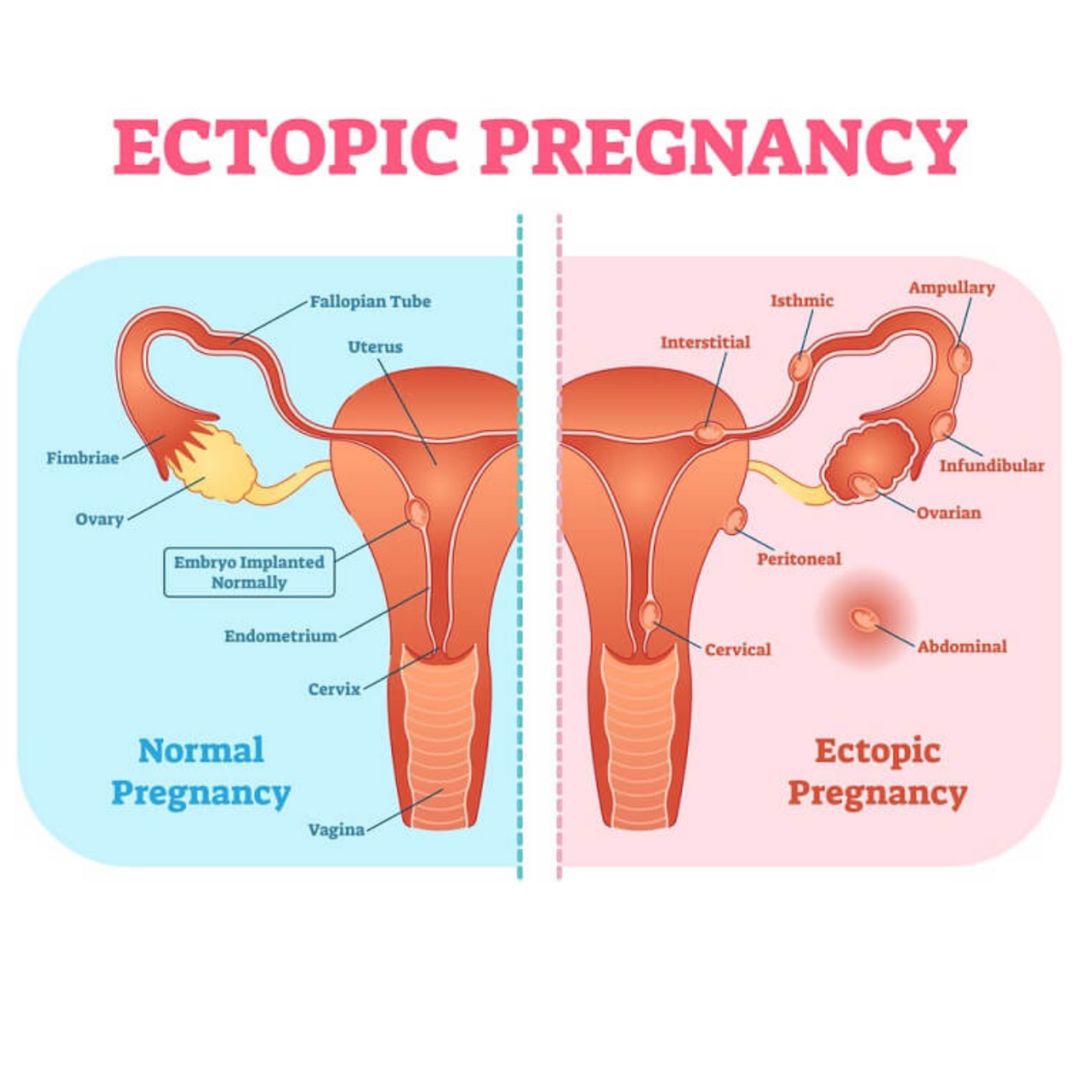
ECTOPIC pregnancy is a pregnancy outside the uterus . It can be in the Tubes ,Ovaries, Cervix, Abdominal or Scar of previous Caesarean section.
Delayed Childbearing: Women are increasingly delaying childbirth for various reasons, such as pursuing education, career goals, or personal choices. Advanced maternal age is associated with a higher risk of ectopic pregnancies.
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART): Fertility treatments, including in vitro fertilization (IVF), can increase the risk of ectopic pregnancies. The manipulation of the reproductive process and the higher likelihood of multiple pregnancies associated with fertility treatments contribute to this risk.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): Infections, particularly sexually transmitted infections (STIs), can lead to inflammation and scarring of the fallopian tubes. PID increases the risk of ectopic pregnancies because the fertilized egg may encounter difficulty passing through scarred or partially blocked tubes.
- Tubal Surgery: Previous surgeries on the fallopian tubes, such as tubal ligation or surgery to correct tubal abnormalities, can increase the risk of an ectopic pregnancy.
- Contraceptive Methods: While contraceptive methods, when used correctly, are effective in preventing pregnancies, failure rates can occur. If a woman becomes pregnant while using an intrauterine device (IUD) or progestin-only contraceptive methods, there is a higher likelihood of it being ectopic.
- Changes in Reproductive Patterns: Societal and lifestyle changes, including changes in sexual behaviours and contraceptive practices, can influence the patterns of pregnancies. These changes may contribute to variations in ectopic pregnancy rates.
Diagnosing Ectopic Pregnancy:
Clinical History and Physical Examination: There is atypical history of missed periods followed by off and on bleeding and pain.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be conducted to measure the levels of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG). In a normal pregnancy, HCG levels typically rise. In an ectopic pregnancy, HCG levels may not rise as expected, or they may plateau or even decrease.
- Ultrasound: Transvaginal ultrasound is a common imaging technique used to visualize the reproductive organs. This method can help identify the location of the gestational sac and determine if the pregnancy is ectopic.
- Doubling Time of HCG: Monitoring the rate at which HCG levels increase over time can provide additional information. In a healthy pregnancy, HCG levels usually double every 48 to 72 hours. Slower-than-expected doubling may suggest an ectopic pregnancy.
Early diagnosis and intervention are essential for treating ectopic pregnancies, as they can be life-threatening if left untreated. If you suspect an ectopic pregnancy or are experiencing symptoms such as abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, or dizziness, it's crucial to seek prompt medical attention. Always consult with a healthcare professional for advice tailored to your specific situation.
Ectopic pregnancy is a medical emergency that requires prompt attention and treatment as it can lead to serious complications. The primary goal of treatment is to remove the ectopic pregnancy and prevent life-threatening complications. Here are the common treatment options:
- Surgery:
- Laparoscopic surgery is a common approach for treating ectopic pregnancies. It involves making a small incision and using a tiny camera and specialized instruments to remove the ectopic pregnancy.
- In some cases, open abdominal surgery (laparotomy) may be necessary, especially if there is severe damage or bleeding.
- Combination Therapy:
- In some cases, a combination of surgery and medication may be used, especially if the ectopic pregnancy has caused significant damage or if the patient is at high risk.
- Follow-up Monitoring:
- After treatment, it's crucial for the healthcare provider to monitor the patient closely to ensure that the treatment was successful and to watch for any signs of complications.
It's important to note that the choice of treatment depends on factors such as the size and location of the ectopic pregnancy, the patient's overall health, and the presence of symptoms or complications. Timely intervention is critical to prevent the rupture of the fallopian tube, which can lead to severe internal bleeding and shock.
If someone suspects they have an ectopic pregnancy or experiences symptoms such as abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, or shoulder pain, they should seek medical attention immediately. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.


